
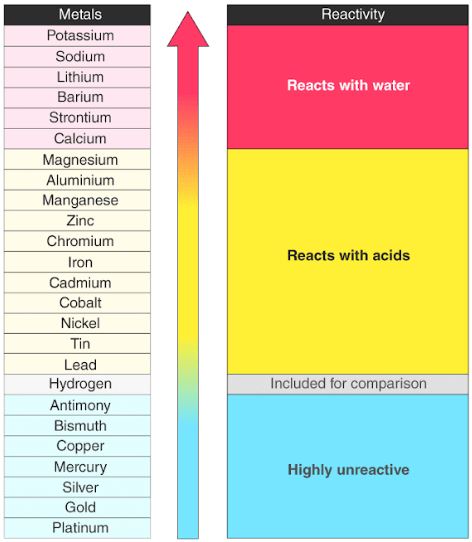
(a) What is a period in a periodic table? How do atomic structures (electron arrangements) change in a period with increase in atomic numbers from left to right?(b) How do the following change on going from left to right in a period of the periodic table? (i) Chemical reactivity of elements (ii) Nature of oxides of elements Give examples in support of your answer.Give examples of alkaline metals present in Group-1 in the Periodic Table.on moving down in a group of the periodic table. (d) On going down in a group in the periodic table, the metallic character of elements. (a) How does the chemical reactivity of alkali metals vary on going down in group 1 of the periodic table (b) How does the chemical reactivity of the halogens. (c) On moving form right to left in the second period, the number of valency electrons.
(b) In going across a period (right to left) in periodic table, the atomicExplain with the diagram:(a.) If the angle between the applied force and the displacement caused due to the force is 0°, then the displacement is in the same direction of the applied force.(b.)If the angle between the applied forc size of the atom.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements:(a) The horizontal rows in a periodic table are called. (a) What is the usual number of valence electrons and valency of group 18 elements of the periodic table?(b) What happens to the number of valence electrons in the atoms of elements as we go down in a group of the periodic table?. (a) On which side of the periodic table will you find metals?(b) On which side of the periodic table will you find non-metals? (c) What is the name of those elements which divide metals and non-metals in the periodic table?. Which one of the following statements is not correct about the trends in the properties of the elements of a group on going down in a group?The chemical reactivity of metals increases.The metallic character of elements increases.The size of the atom increases.The valence electrons increase. How does the number of valence electrons vary on moving from left to right:(i) In the first period of the periodic table? (ii) In the second period of the periodic table?. Write an example of a compound formed with(a) chlorine (Group 17 of Periodic Table)(b) oxygen (Group 16 of Periodic Table) Carbon, Group (14) element in the Periodic Table, is known to form compounds with many elements. State whether the following statement is true or false:On-going down in a group of the periodic table, the number of valence electrons increases. (a) How does the size of atoms (atomic size) generally vary in going from left to right in a period of the periodic table? Why does it vary this way?(b) What happens to the metallic character of the elements as we move from left to right in a period of the periodic table?. Halogens belong to group _ of the Periodic Table. Metals with high atomic numbers tend to be more reactive as their electrons are far from the positively charged nucleus, so, they can be removed easily. Metals form positively charged ions as they tend to lose electrons. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements? Explain your answer. The reactivity of metals is because of their incomplete outer orbitals or due to their electronic configuration. (a) How does the atomic size vary on going down from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table? Why does it vary this way?(b) Lithium, sodium and potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. (a) How does the tendency to lose electrons change as we go down in group 1 of the periodic table? Why does it change this way?(b) How does the tendency to gain electrons change as we go down in group 17 of the periodic table? Why does it change this way?. (a) How does the electropositive character of elements change on going down in a group of the periodic table?(b) State how the valency of elements varies (i) in a group, and (ii) in a period, of the periodic table. How does the valency of elements vary in going down a group of the periodic table?. Predict the melting and boiling points of astatine, and its state at room temperature. 
Astatine is placed below iodine in group 7. The graph shows the melting and boiling points of the first four group 7 elements.

more energy is needed to overcome these forces.the intermolecular forces become stronger.In group 7, the further down the group an element is, the higher its melting point and boiling point. The table shows the colour and physical states of chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature. In all groups of the periodic table, the further down the group an element is, the higher its relative molecular mass. Each molecule is made up of a pair of halogen atoms joined by a single covalent bond. The halogens show trends in their physical and chemical properties. Group 7 is on the right-hand side of the periodic table, next to group 0 The elements in group 7 are called the halogens. Group 7 contains non-metal elements placed in a vertical column on the right of the periodic table.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
